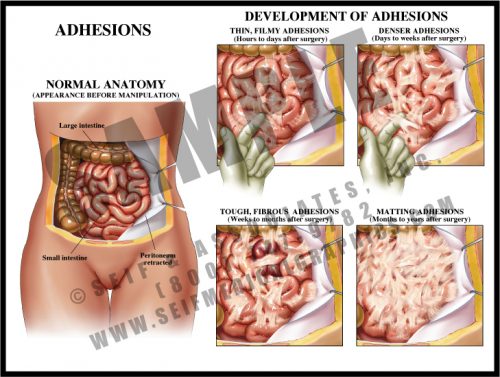
- Adhesions are fibrous scars which can form after any disturbance within body cavities and spaces. Inciting events can include surgery, trauma, and inflammation.
- Within hours of disturbance, thin, filmy strands form between bowel loops and between bowel and peritoneum and/or body wall. These continue to form for a period of time and mature over a period of weeks.
- Mature adhesions are dense, white fibrous tissues which have merged with the outer layer of the tissues; they eventually develop their own blood supply and may become severe enough to cause chronic pain and pose a chronic risk of small bowel obstruction or volvulus.
-
-
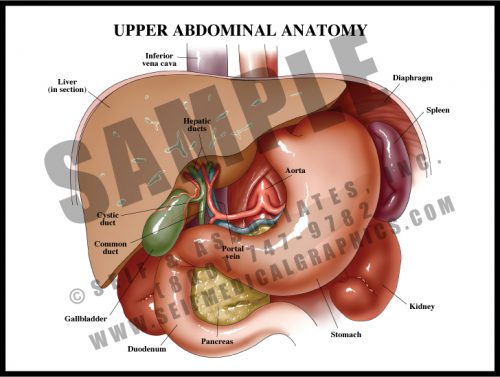
- The primary function of the upper abdominal organs is the breakdown of food for distribution by the small bowel. Chewed and macerated food travels through the esophagus to the stomach, where strong acids and muscular contractions break it down further.
- Proteolytic enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver and gallbladder drain into the duodenum to further the digestion and breakdown of food.
- The spleen functions as part of the hematopoietic system, controlling the distribution and eventual destruction of red blood cells. It also acts as a part of the immune system.
- Blood is supplied to most of these structures by branches of the celiac trunk, the first major aortic branch in the abdomen.
-
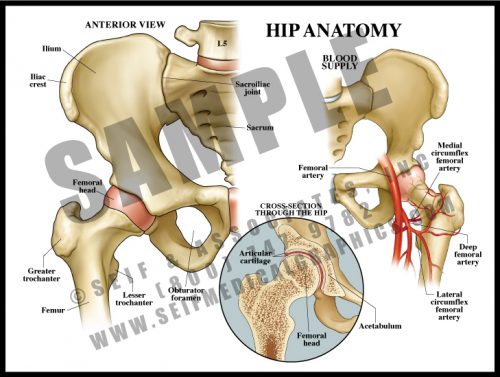
- The largest joint in the body, the hip is composed of the large, round head of the femur which lies within the acetabulum or cup of the pelvis. Cartilage covers the articular surfaces, as in every other joint. There is a joint capsule and a number of muscles which cross and protect the joint and allow movement in a number of planes.
- The blood supply to the hip is relatively meager and easily disrupted with trauma.
- Since the entire weight of the body goes through this joint with every step, it is vulnerable to damage from use and is a common site for degenerative joint disease.
-
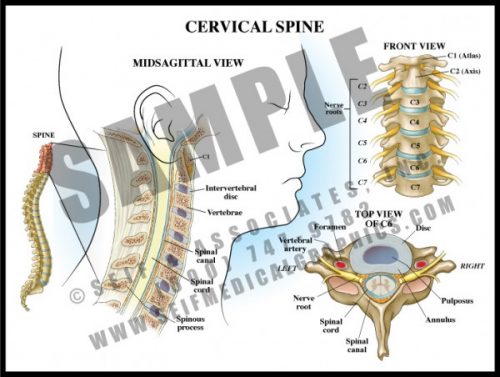
- The 7 vertebrae of the cervical spine help support the skull and protect the spinal cord as it exits the cranium to pass downward through the spinal canal.
- The transverse processes each have a small hole through which the vertebral arteries pass to join to form the basilar artery supplying the posterior and deep portions of the brain and brainstem.
- The cervical nerve roots form the brachial plexus which supplies sensation and movement to the upper extremities.
- Degenerative joint disease and disc disease are very common in the cervical spine, leading to arm and hand pain and dysfunction requiring decompression and sometimes fusion.
-
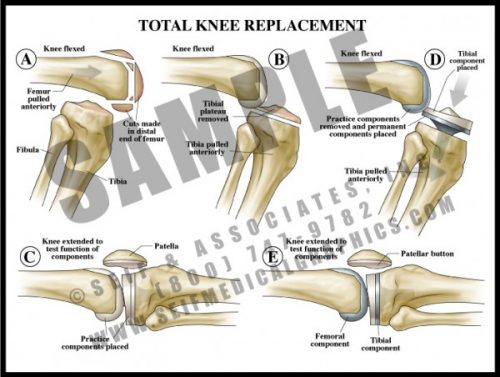
- One of the more common surgical procedures, diseased bone and articular surfaces (usually from either trauma and/or degenerative joint disease) are surgically removed.
- Most knee prostheses are made of a strong metal with a durable plastic overlay to serve as a joint surface.
- As with any bony prosthesis, these can be either cemented into place or have a roughened surface which allows bone to grow into the surface.
- All three units (femoral, tibial and patellar) can be inserted together or individually, depending upon the specific needs of the patient.
-
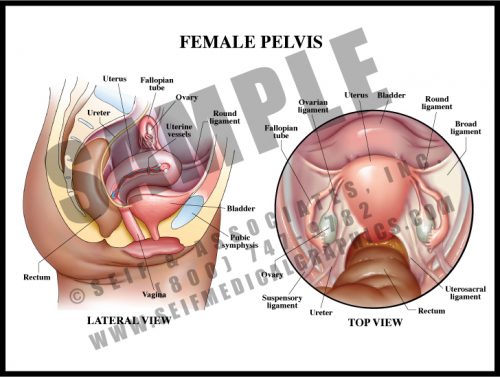
- The female pelvis contains the bladder, uterus, vagina, and rectum. The tissue between the vaginal and rectal openings is a tight collection of tendons from the pelvic floor muscles, the perineum. The entire region is called the vulva.
- The non-pregnant uterus is about the size of a small pear. It is a hollow muscular organ, its neck enclosed by a thick circular muscle known as the cervix.
- Urine is excreted from the kidneys via the ureters, which transport it to the bladder. It is then carried to the outside by the relatively short urethra.
- The ovaries release ova (eggs) each month to the uterus via the fallopian tubes; ovarian hormones are absorbed into the bloodstream.
- The organs are held in the pelvis by a number of ligaments connecting them to the pelvic walls.
-
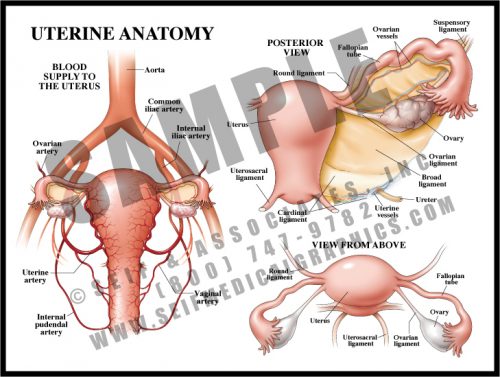
- The uterus is small and contracted in its non-pregnant state, but grows to fill nearly the entire abdomen during pregnancy. Delivery is effected by repeated strong contractions pushing the fetus through the cervix and out the birth canal (vagina).
- The fallopian tubes carry the ova to the uterine cavity, where fertilized eggs implant and develop.
- The blood supply to the uterus is redundant and increases greatly during pregnancy.
-
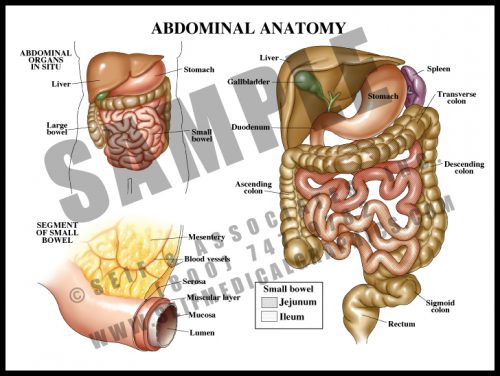
- The contents of the abdomen are primarily associated with digestion and distribution of nutrients.
- The esophagus, a tube which carries food and fluid through the thorax, enters the abdomen through the diaphragm, where it widens into the stomach; the stomach empties into the small bowel (duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, in which food is absorbed into the blood stream), and from there into the large bowel, where waste material is compacted as fluid is reabsorbed into the system.
- The liver has multiple functions affecting a number of other body systems, including digestive, hematologic and endocrine/metabolic.
- The large and small bowels are supplied by branches off of the aorta carried within the mesentery, a double-layered sheetlike structure.