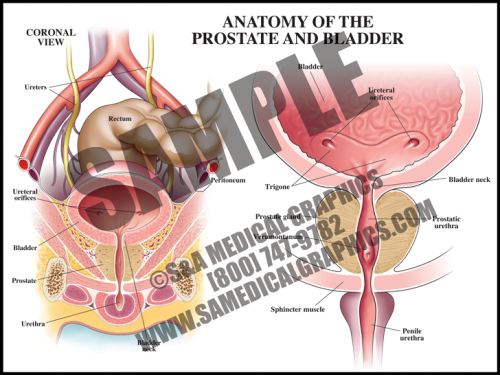
- The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located between the bladder and the penis; it secretes fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. The male urethra runs through the center of the prostate, from bladder to penis.
- The bladder is a hollow, muscular organ in the lower abdomen that stores urine and allows urination to be infrequent and voluntary.
- It is not uncommon for older men to develop benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), in which the prostate becomes enlarged, resulting in restriction of the ow of urine through the urethra. The prostate can also develop cancer, although that is much less common than BPH.
-
-
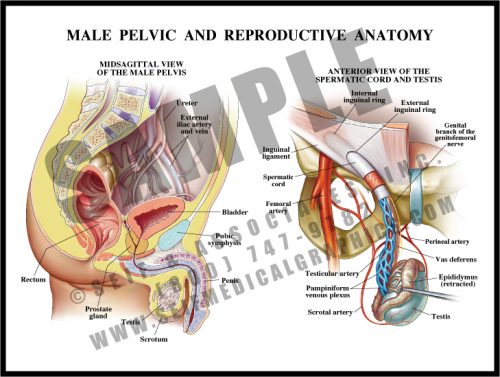
- The male pelvis contains the bladder and rectum, along with the internal portions of the reproductive system: the prostate, seminal vesicles, and the intrapelvic portions of the ductal apparatus.
- Sperm is produced in the testes, which lie in the scrotal sac outside of the pelvis. The sperm travels up the spermatic duct and is stored in the seminal vesicles. At ejaculation, sperm is released along with prostatic fluid, both of which travel down the urethra.
- The urethra has three parts: the prostatic portion; the membranous portion which passes through the urogenital diaphragm, and the penile portion.
- The spermatic cord contains a venous plexus, the spermatic artery and the spermatic duct.
-
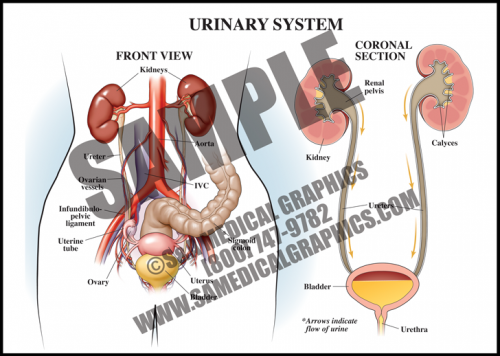
- The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. This system is responsible for removing wastes and extra fluid from the body in the form of urine. It also keeps the levels of electrolytes in the body stable.
- The kidneys filter the blood through specialized capillaries in order to remove waste materials and produce urine.
- The ureters drain urine from the kidneys and transport it to the bladder, where it is stored until it is released outside the body through the urethra during urination.